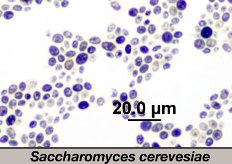
Common species are as follow:
S. bayanus
S. boulardii
S. bulderi
S. cariocanus
S. cariocus
S. cerevisiae
S. chevalieri
S. dairenensis
S. ellipsoideus
S.eubayanus
S.exiguus
S.florentinus
S.kluyveri
S. martiniae
S. monacensis
S.norbensis
S. paradoxus
S.pastorianus
S.spencerorum
S.turicensis
S.unisporus
S.uvarum
S.zonatus
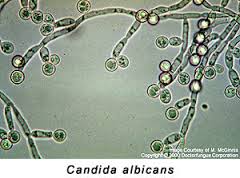
The Common species are as follow:
C. albicans
C. ascalaphidarum
C. amphixiae
C. antarctica
C. argentea
C. atlantica
C. atmosphaerica
C. blattae
C. bromeliacearum
C. carpophila
C. carvajalis
C. cerambycidarum
C. chauliodes
C. corydali
C. dosseyi
C. dubliniensis
C. ergatensis
C. fructus
C. glabrata
C. fermentati
C. guilliermondii
C. haemulonii
C. insectamens
C. insectorum
C. intermedia
C. jeffresii
C. kefyr
C. keroseneae
C. krusei
C. lusitaniae
C. lyxosophila
C. maltosa
C. marina
C.membranifaciens
C. milleri
C. mogii
C. oleophila
C. oregonensis
C. parapsilosis
C. quercitrusa
C. rugosa
C. sake
C. shehatea
C. temnochilae
C. tenuis
C. theae[20]
C. tolerans
C. tropicalis
C. tsuchiyae
C.sinolaborantium
C. sojae
C. subhashii
C. viswanathii
C. utilis
C. ubatubensis
C. zemplinina
Candida wickerhami
C.gulliermondii
C. shehatae
C. cylindracea
Application in engineering
Candida albicans has been used in combination with carbon nanotubes (CNT) to produce stable electrically conductive bio-nano-composite tissue materials that have been used as temperature sensing elements. Candida is used in production of Autoantibiotics, Citric Acid, Phynyl alcohol,Biomass,Iditol,Food Yeast, Deaminase, Riboflavin,Lipase and Mannitol. Assay of Amphotericin-B, Antimicrobial activity,and Amphotericin-B.This Yeast is used in degradation of Cellobiose, Hydrocarbons, Cellodextrins, D-Xylose and Phenolic wastes. Oxidation/Utilisation of Phenol and Catechol, Uric acid.
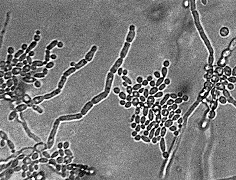
Common species are as follow:
T. aquatile
T. asahii
T. asteroides
T. brassicae
T. caseorum
T. chiarellii
T. coremiiforme
T. cutaneum
T. debeurmannianum
T. dehoogii
T. dermatis
T. dohaense
T. domesticum
T. dulcitum
T. faecale
T. gamsii
T. gracile
T. guehoae
T. inkin
T. insectorum
T.japonicum
T. jirovecii
T. lactis
T. laibachii
T. lignicola
T. loubieri
T. moniliiforme
T. montevideense
T. mucoides
T.multisporum
T. ovoides
T. porosum
T. scarabaeorum
T. sinense
T. smithiae
T. sporotrichoides
T. terricola
T. tryphenardum
T. vadense
T.vanderwaltii
T. veenhuisii
T. wilphenae
Common species are as follow:
P. farinosa
P.pastoris
P.stipitis
P.angusta
P.minuta
P.anomala
P.jadinii
P.haplophila
P.capsulata
P.cellobiosa
P. heedii
P. guilliermondii
P. kluyveri
P.membranifaciens
P. norvegensis
P. ohmeri
P. pastoris
Pichiamethanolica
Pichia is used in production of Glycerol, Xylitol, single cell protien, Amylase, 2,3-Butanediol,Citric acid, B-Galatosidase and single cell protein. This Yeast is also used in Oxidation/Utilization of Autotrophic Hydrocarbons, Methanol, Propane.
Fermentation of Xylose. Degradation of D-Xylose.
Pichia is widely used for protein expression using recombinant DNA techniques. Hence it is used in biochemical and genetic research in academia and the biotechnical industry.
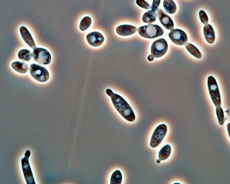
Common species are as follow:
Y. bubula
Y. deformans
Y. lipolytica
Y. porcina
Y.yakushimensis
It is used in industrial microbiology, especially for the production of specialty lipids Isocitric acid, Phosphatase, and Yeast protein.It is also used in degradation of Hydrocarbons.

Common species is
R.toruloides
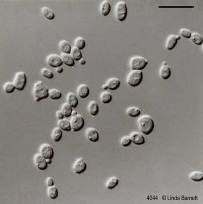
Common species is
P. tannophilus
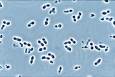
Kluyveromyces is a genus of ascomycetous yeasts in the family Saccharomycetaceae and belongs to Ascomycotina. Some of the species, such as K. marxianus, are the teleomorphs of Candida species and belongs to Ascomycotina..
Common species are as follow:
Kulyveromyces fragilis
Kulyveromyces marxianus var. lactis
K. aestuarii
K. africanus
K. bacillisporus
K. blattae
K. dobzhanskii
K. hubeiensis
K. lactis
K. lodderae
K. nonfermentans
K. piceae
K. sinensis
K. thermotolerans
K. waltii
K. wickerhamii
K. yarrowii
It is used in production of and Induction of B-galactosidase and assay of Thiamine.
Metschnikowia is a genus of yeast in the family Metschnikowiaceae and belongs to Ascomycotina.
Common species are as follow:
M. pulcherrima
M. cubensis sp. Nov
M. pulcherrima

Zygosaccharomyces is a genus of yeast in the family Saccharomycetaceae and belongs to Ascomycotina.
Common species are as follow:
Z. bailii
Z. bisporus
Z. cidri
Z. fermentati
Z. florentinus
Z. kombuchaensis
Z. lentus
Z. mellis
Z. microellipsoides
Z. mrakii
Z. pseudorouxii
Z. rouxii

Common species are as follow:
S. castellii
S. capriottii
S.etchellsii
S. yamadae
S.occidentalis
The genus Oosporidium, introduced by Stautz in 1931, has been considered a synonym of the genus Trichosporon by Buchwald and belongs to Ascomycotina.
Common species is
O. margaritiferum
Common species are as follow:
D. anomala,
D. bruxel- lensis
D. custersiana
D. naardenensis
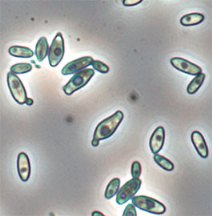
Hanseniaspora is a genus of yeasts. The name Kloeckera is applied to its anamorph form. They are typically apiculate in shape and often found in grape musts pre-fermentation.
Common species are as follow:
Kloeckera apiculata
H. guilliermondii
H. occidentalis
H.osmophila
H. uvarum
H. valbyensis
H.vineae
Kloeckera lindneri
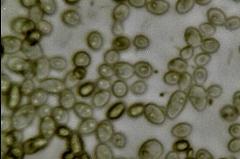
Torulaspora is a genus of ascomycetous yeasts in the family Saccharomycetaceae and belongs to Ascomycotina.
Common species are as follow:
T.delbrueckii
T. franciscae
T. globosa
T. pretoriensis


Monascus is a genus of mold. Among the 24 known species of this genus, the red-pigmented Monascus purpureus is among the most important and belongs to Ascomycotina.
Common species are as follow:
M. albidulus
M. argentinensis
M.aurantiacus
M.barkeri
M. bisporus
M. eremophilus
M. floridanus
M. fuliginosus
M.fumeus
M. kaoliang
M. lunisporas
M. mucoroides
M. olei
M. pallens
M.paxii
M.pilosus
M.pubigerus
M. purpureus
M. ruber
M.rubropunctatus
M. rutilus
M. sanguineus
M.serorubescens
M.vitreus